About three years ago, my staff noticed that our surgical patients who participated in The DOC Journey principles were doing much better. The outcomes were more consistent, and we were seeing fewer failures. The postoperative pain was more easily controlled. Patients were moving forward quickly with rehab while re-entering a normal life. Additionally, their anxiety often dramatically improved.
We decided that if the surgical results were so much better, we would have all of our patients engage in at least 8 to 12 weeks of “prehab” before any surgery, regardless of the magnitude. Our protocol included:
- Learning about chronic pain through my book, Back in Control: A Spine Surgeon’s Roadmap Out of Chronic Pain.
- They were sleeping at least six hours a night (often required meds).
- Addressing their stress.
- Engaging in the expressive writing exercises.
- Learning and using active meditation.
- Noting some improvement in their mood and pain.
- Narcotic medications were defined and stabilized.
We encouraged them to return, but we weren’t going to perform surgery without them engaging in a prehab process.. The data shows that not addressing these issues significantly compromises surgical outcomes. (1)
What Happened?
I am enjoying my practice at a level that I could not have imagined. Our patients are doing well and excited about their progress. What I didn’t expect was that so many patients would become pain-free without undergoing surgery I thought they needed. We presented a research paper reporting on a group of patients who’d come in for their final preoperative visit, and their pain was gone. Of course, we canceled the surgery.
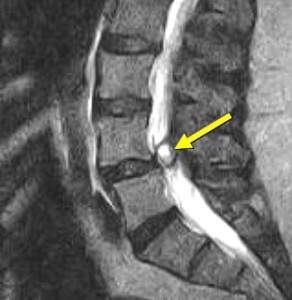
What was even more surprising was the severity of the problems. Normally, the diameter of the spinal canal is about 15 mm. I don’t schedule surgery unless the canal is less than 8 mm, and the patient has leg pain. I have one patient who avoided surgery with a four mm canal.
Janet’s Story
The following letter is from a woman whom I saw last summer with a large synovial cyst. This is a problem where a sac of fluid is formed off a facet joint off the back of the spine. It was not only pinching her sciatic nerve, but it was calcified, which means it couldn’t shrink. I immediately offered her a small operation to remove it. The outcome of removing the cyst is predictably positive with few complications. It is one of my favorite procedures. I offered her the prehab process through my book and website. I also thought the pain center would help. I was surprised that she did not immediately take me up on surgery. She never returned to see me, and I received this letter from her about eight months later.
Dear Doctors,
Last summer, an MRI scan revealed a synovial cyst in my back. I had severe pain from cramps in my butt and calf muscles. My family doctor referred me to your office.
I am writing to update you on my status, which is greatly improved. On my initial visit at the Pain Center, the doctor asked me to keep a journal of what I couldn’t do.
What I cannot do because of pain
I cannot get up in the morning in a flash. I need to exercise and stretch my right leg in bed, roll carefully out of bed to ice my butt and calf, do stair-step exercises, and then finally do a 20 to 30 minute “working with pain” meditation. I can’t sit in any chair I want because my butt muscle will spasm. Car seats are hard to sit in. I have to get out at least every 45 minutes to stretch. I was on Gabapentin, Cyclobenzaprine, and Ibuprofen. I followed the Back-in-Control program, writing down my thoughts and beginning to focus on what I wanted to do, including returning to dance class. In early October, I began sleeping in a semi-upright position, with a pillow under my legs, and the cramping began to subside. I also had biofeedback training. By mid-November, I was able to get off all pain medications and start lifting weights again.
I have very occasional twinges in my right butt when sitting or walking, but I am basically pain-free. I am so grateful for the chronic pain management program and extremely grateful that you offered the program rather than immediate surgery on the synovial cyst.
Many, many thanks.
Sincerely,
Janet
Do Surgery Now??
I had forgotten about her case, so I reviewed her MRI scans and was shocked to see the size of the cyst. However, I have been surprised at the severity of the pathology with every surgical patient I have witnessed becoming pain-free without an operation. In fact, in the first edition of my book, I comment that if a patient has a significant structural problem with matching symptoms, surgery should be performed quickly so as to move forward with the comprehensive rehab program. I thought the pain would be too distracting to be able to participate. The opposite scenario occurred in that when I performed surgery in the face of a fired-up nervous system, the pain would frequently be worse. I eventually discovered this problem has been well-documented in the medical literature. (1) Chronic pain can actually be induced or worsened as a complication of any surgical procedure, including painless ones such as a hernia repair. One of the risk factors is pre-existing chronic pain in any part of the body.
I now have dozens of stories similar to Janet’s. There are many times that I do perform urgent surgery for compelling problems. But if there’s any room to have my patient participate in the prehab, that is what we have them do.
Video: Get it Right the First Time
Ask for This Approach!
I’m excited about this turn of events, although it is becoming a little challenging maintaining a surgical practice. The medical literature has clearly documented that this process is effective. Ask your doctor to help you out with setting up your own program. You don’t need a major pain center, as the necessary resources are readily available.
Every surgery has risks, and no one thinks a complication will happen to him or her. I have seen them all. They are unpredictable, and the outcomes can be catastrophic. Also, why would you not want to maximise your odds of success. Do you really need surgery? Be careful!!
Perkins FM and Henrik Kehlet. “Chronic Pain as an Outcome of Surgery.” Anesthesiology (2000); 93: 1123-1133.
